
During a short PTO, I found myself reflecting on the AI Hallucination topic that has been popping up in recent discussions I had with the team over the last couple of months while building several support use cases. It's easy to assume everyone working on AI LLMs, applications, or integration layers has already covered this ground. But sometimes, going back to basics is the most effective way to spark new ideas.
Here's a quick breakdown of what AI hallucinations are and how we might think about tackling them:
Types of Hallucinations
What are the common categories of hallucination then?
The system generates objectively incorrect or made-up/fabricated facts. This often emerges from gaps or errors in the training data. Think of a RAG system with poor retrieval quality or irrelevant/missing documents, so it simply fills in the blanks.
Output examples: generating API method that doesn't exist in the library or a citation that doesn't exist.
The system response is inconsistent with the context of the prompt, even if the facts themselves might be correct in another context. The model misinterprets the prompt or lacks proper guidance.
Mitigation: Structured prompt engineering, combined with RAG can add clarity.
The output is logically flawed. Common patterns include:
- Contradicting logic
- Invalid reasoning (All apples are fruits; some fruits are bananas; therefore, all apples are bananas.)
- Math errors (5+7=11)
def is_even(n):
if n % 2 == 1:
return True
else:
return FalseThere's no syntax error, however the function is named is_even, but it returns True when n % 2 == 1 (when n is odd). It returns False when n is even — this is the opposite of the intended behavior.
Multimodal refers to the situation when the model works with more than a single Input/Output type (text/audio/video/image). This type of hallucination emerges when the system generates fabricated or incorrect information across the different modals.
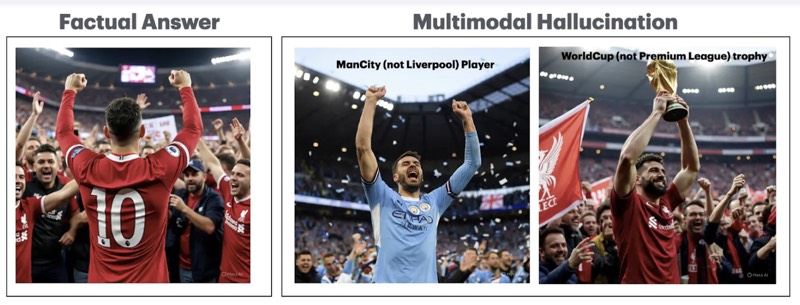
Measuring Hallucinations
There's no silver bullet yet, but common practices include:
Human Evaluation/Labeling
Assessing the Hallucination Rate (HR), defined as the number of hallucinatory outputs divided by the total number of AI outputs.
Factual Accuracy Metrics
Precision = TP / (TP + FP)
Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
BERTScore
Measures semantic similarity between generated and reference texts (good for catching irrelevant content, but doesn't assess factual truth or logic).
Taxonomy of Hallucination Mitigation Techniques
From the grand scheme of things, we need to focus on:
Enhancing Training Data Quality
Comprehensive datasets, data cleansing, bias removal & continuous data improvements/updates
Validation
Human review, feedback loops & real-time similarity scores (ex: BERTScore)
Refined Prompt Engineering
Clear/specific prompts plus specific desired output format
Using RAGs
Retrieve relevant data and augment LLM knowledge with additional, often private or real-time data not part of the model's original training data
The RAG Process:
In a detailed manner, this academic paper presents a structured taxonomy of hallucination mitigation techniques, categorizing approaches based on key dimensions and offering a solid foundation for both researchers and practitioners working to improve model reliability.
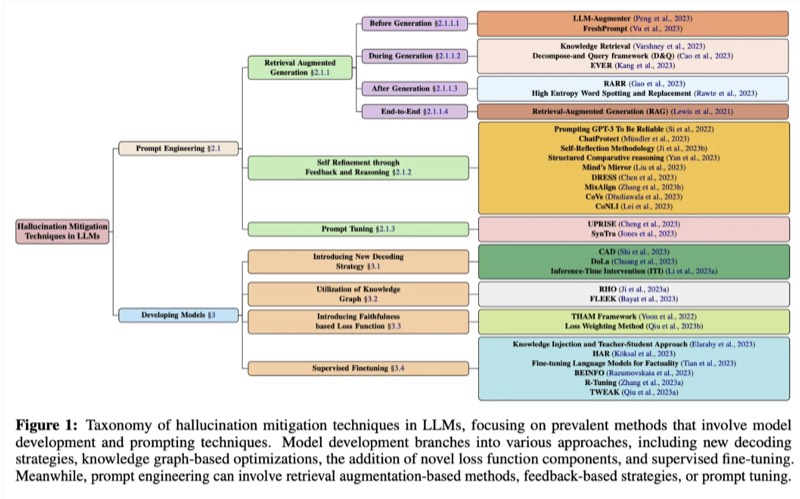
Source: Lee, C., Han, X., Wu, Y., Lee, K., Cheng, M., Yang, Y., & Tan, C. (2024)